Legislation starts off as a Bill. This merely means that the legislation is in draft form. Bills can be proposed by members of the House of Commons (MPs) or by members of the House of Lords. Bills can either be (a) public Bill or (b) Private members’ Bill. A public Bill is one which affects the entire population and is introduced by a government minister. A private members’ Bill is introduced by a Lord or an MP who is not a government minister. However, if the bill goes on to become law it will affect the entire population. Private members' Bills usually come about because some current issue is important and has attracted the attention of a pressure group which then lobbies an MP for change. Examples of pressure groups are the Citizens Advice Bureau, and “Which?”.
There are three ways in which a Private members Bill can be proposed:
-
A ballot procedure allows a maximum of 20 back-benchers to propose new legislation. However, the timeframe for Parliament to process new legislation means that there is only a small quota of legislation allowed to be introduced by back-benchers. At the beginning of each parliamentary session the 20 members who were successful in the ballot are allowed to present their proposed legislation. Each of the private members’ Bills are usually discussed on a Friday and given a provisional date for a second reading or any further stages to be undertaken. These Bills may be of a controversial nature and they tend to relate to a member or a group of members who have a connection with the subject matter. The majority of private members’ Bills are usually done through the ballot procedure.
-
Ten minute rule Bills are allowed under Standing Order No. 23. This order allows members to gain permission to introduce a Bill. The ten minute rule allows members to introduce a subject matter and a proposed change in the law. This process is usually taken up just after question time on a Tuesday. The ten minute rule was used by the MP Alex Cunningham to introduce a Bill which proposed a ban on smoking in private vehicles where there are children under the age of 18 years old present. Pressure groups such as the British Lung Foundation (BLF) have supported this proposal through their campaign against smoking in cars where children are present.
- An MP is permitted to introduce a Bill after giving notice under what is known as Standing Order No. 57. This type of Bill cannot be presented until after all the ballot bills have been presented and they have reached the second reading stage.
[The Open University, 2014]
The Abortion Act 1967 is an example of a Private members' Bill that became law.
The Law Commission and Criminal Cases Review Commission (CCRC) may also suggest changes to the law.
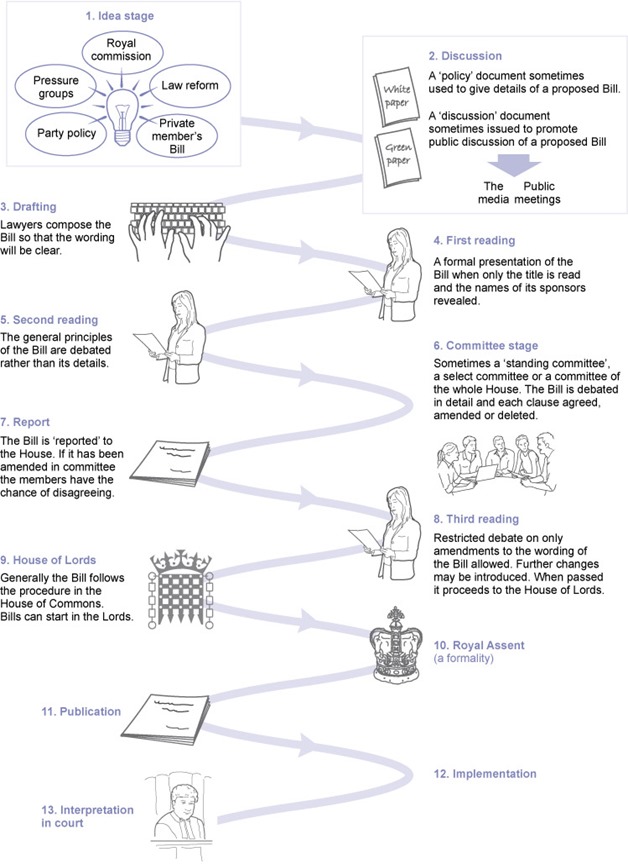
Stages of a Bill
The stages that a Bill that has to go through before it becomes law is fully described here.
© The Open University
No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments that are rude, impolite or attacking anyone will not be posted. Spam will be deleted. Choose a screen name, anonymous comments risk censor.